What are the Whitespaces of Cultivated Meat and How Can Farmers Contribute?
This post is also available in:
This post is also available in:
![]() Ελληνικά (Greek)
Ελληνικά (Greek)
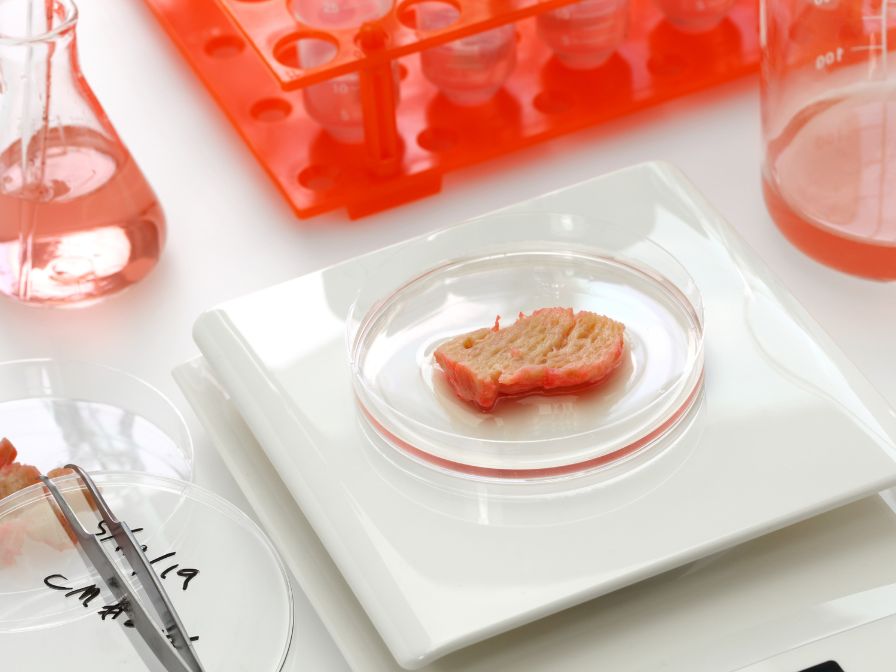
Cell-cultivated meat is an emerging technology that has the potential to transform the way we produce and consume meat. By growing animal cells in a lab setting, cell-cultivated meat offers a more sustainable and ethical alternative to traditional meat production. However, farmers can contribute to several whitespaces in the development and commercialization of cell-cultivated meat that.
Advancing Sustainable and Cost-Effective Growth Media for Cell-Cultivated Meat
One whitespace in cell-cultivated meat is the development of new growth media that are more sustainable and cost-effective than current options. Growth media are the nutrients and other substances that cells need to grow and proliferate in a lab setting. Many current growth media are derived from animal sources, such as fetal bovine serum, which is expensive and not sustainable in the long term.
Farmers can contribute to this whitespace by developing plant-based, sustainable, and cost-effective crops for new growth media that are. For example, soybean and pea protein isolates have been suggested as potential alternatives to animal-derived growth media. Farmers could also explore the use of waste products from their crops, such as corn or wheat, to create new growth media for cell-cultivated meat.
Advancing Scalable Bioreactor Systems for Commercial Cell-Cultivated Meat Production
Another whitespace in cell-cultivated meat is the development of scalable bioreactor systems. Bioreactors are the vessels in which cells are grown and multiplied in a lab setting. Current bioreactor systems are often complex and expensive, limiting cell-cultivated meat’s scalability and commercial viability. Farmers can contribute to this whitespace by developing new bioreactor systems that are more scalable, efficient, and cost-effective. For example, vertical farming techniques could be adapted to the production of cell-cultivated meat, allowing for high-density and automated growth of cells. That way the expertise of already experienced vertical farmers could be applied for the purposes of cell-cultivated meat. Farmers could also explore the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to power those bioreactor systems.
Pioneering the Path: Farmers and Breeders can shape Regulatory, Genetic, and Sourcing Landscapes for Cell-Cultivated Meat
Farmerscan contribute to the whitespace of regulatory and legal frameworks for cell-cultivated meat. As a new and innovative technology, cell-cultivated meat may face regulatory and legal hurdles in some countries or regions. Farmers can work with policymakers and other stakeholders to advocate for supportive regulatory and legal frameworks enabling cell-cultivated meat development and commercialization.
Farmers/breeders can also contribute to the development of cell-cultivated meat by providing high-quality and well-characterized animal cells that can be used in the lab. Breeding programs can select animals based on their genetic traits, such as growth rate, muscle development, and fat composition, which could be desirable for cell-cultivated meat production. Additionally, breeders can help researchers develop new cell lines that are more efficient and cost-effective for meat production. Breeding programs can also inform the development of regulatory and legal frameworks for cell-cultivated meat by providing insights into animal genetics and breeding practices. Overall, breeders can serve as a valuable resource for the cell-cultivated meat industry in terms of cell sourcing and genetic optimization.
In conclusion, there are several whitespaces in the development and commercialization of cell-cultivated meat that farmers can contribute to. By developing new growth media, and scalable bioreactor systems and advocating for supportive regulatory frameworks, farmers can help accelerate the development and commercialization of cell-cultivated meat. Additionally, by educating consumers and working with chefs and restaurants, farmers can help drive demand for cell-cultivated meat and create new opportunities for sustainable and ethical food production.
You can read more information regarding Cultivated meat advantages and challenges or whether consuming it is healthy and vegan.
Further reading:
Cellular Agriculture – Cultivated Meat
Cell-cultivated meat advantages and challenges ahead
Is Cultivated Meat Healthy and can Vegans eat it?
What are the Whitespaces of Cultivated Meat and How Can Farmers Contribute?








































































