Smart Packaging Application in Bakery Products
What is the function of food packaging?
Food packaging functionality is experiencing rapid development in line with consumer needs for food quality and safety. Consumer awareness of food quality and safety can be increased by understanding the information provided by labels on food packaging. The label on the packaging provides information related to the ingredients used in the product formulation, nutritional content, serving method, and other data that support the product supply chain to be maintained properly. Packaging has a functional value that can be categorized based on the type of packaging material and the techniques used in the food packaging process. Packaging materials, technology, and methods selection based on food categories and characteristics ensure that the final product has high quality and safe for customer consumption.
Packaging development has been modified to meet customer demands for quality, safety, and traceability of the food they consume. In addition, an effective and efficient way is needed to meet business needs by maintaining food quality through the supply chain and also reducing food loss and food waste. Future trends that call for a dynamic and quick-paced lifestyle promote lifestyle changes toward the consumption of ready-to-eat food. This encourages innovation in packaging development by increasing product shelf life, providing traceability and packaging that can substitute preservatives in food formulation.
What is meant by smart packaging?
Changes in the packaging function, which at first solely addressed the four primary functions (protection, comfort, container, and communication), have now evolved into functions that guarantee the sustainability of food products throughout the supply chain. This change in function is what drives the transition from conventional packaging to innovative packaging. Traditional packaging applies the selection of material types and packaging techniques to fulfil these four main functions. Innovative packaging can improve, combine and expand the main functions of traditional packaging. One of the innovative packaging used today is smart packaging. Smart packaging is a concept that involves intelligent and active packaging that can monitor internal and external changes that occur in food (intelligent) and further responses (active) by communicating them through an external interface (electrical or optical).
What are the benefits of smart packaging?
The main objectives of implementing smart packaging are to extend shelf life and maintain product freshness, convey information about product quality to consumers, improve product safety, and improve traceability while moving through the supply chain.
Understanding how smart packaging is applied in food as innovative packaging can help package developers achieve their goals. The readiness of science, technology, and the general public to use and benefit from innovative packaging will all play a role in how well smart packaging is developed.
- What strategies need to be followed to support smart packaging development?
- Understanding the differences between innovative packaging and traditional packaging;
- Smart packaging concept
- Consumer’s perspective on smart packaging
- Smart packaging function
Smart Packaging Implementation: Challenges and Opportunities
What is the difference between innovative and traditional packaging?
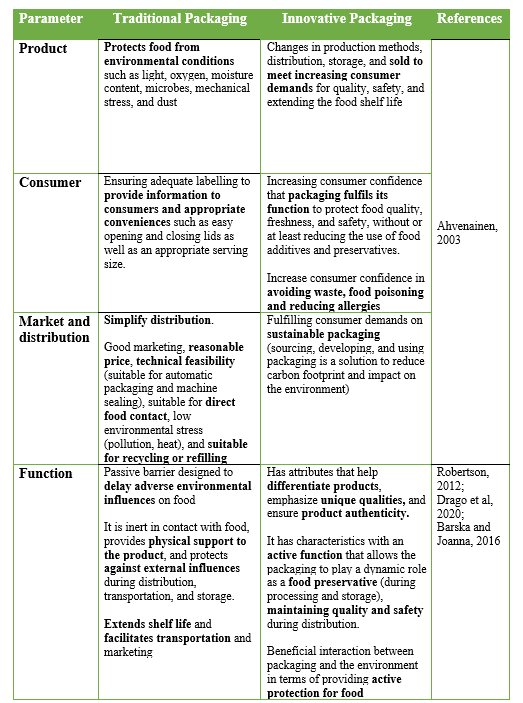
Traditional packaging is no longer in line with increasing consumer expectations, product complexity, and national and international initiatives related to fostering a circular economy and minimizing the carbon footprint of manufactured products. This encourages improved functionality from traditional packaging to innovative packaging that can accommodate the additional needs of various consumers. In other words, innovative packaging is packaging that includes the functions of traditional packaging with increased and expanded functional values adapted to today’s consumer needs. The difference between traditional and innovative packaging can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1. The difference between traditional and innovative packaging
What is the smart packaging?
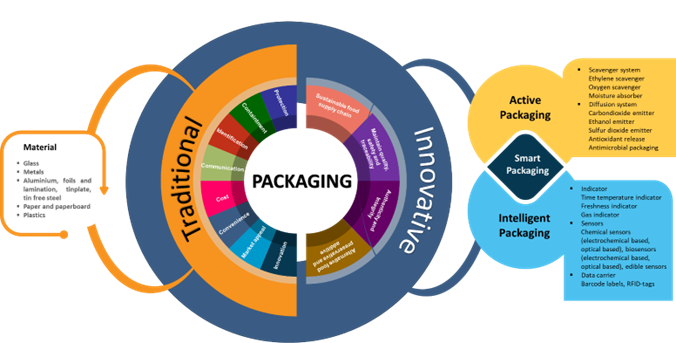
Smart packaging is packaging that has intelligent and active capabilities. It can be applied as a solution to monitor changes in products or the environment (intelligent) and act on these changes (active). Intelligent and active packaging is a packaging combination system that has a functional synergistic effect on smart packaging. Intelligent packaging does not extend the shelf life or improve food quality. However, it can track food quality and provide real-time quantitative information on color changing or other physical parameters. Active packaging is all substances or devices that can extend shelf life or maintain and improve the packaging environment. These substances are intentionally added to packaging to be used for certain functions such as releasing or absorbing CO2, O2, ethylene, odor, flavor, antioxidant, and antimicrobial.
What is intelligent packaging and how does it work?
There are three basic technologies for intelligent packaging systems:
- indications,
- sensors
- data carriers.
Indicators and sensors have the main function of providing information related to product quality, while data carriers are more involved in supply chain logistics management. Indicators’ main function is to send information to consumers regarding the presence or absence of a particular substance, indicate whether a reaction occurs between substances, and monitor the concentration of a particular substance. This information is converted into a signal that appears as an instantaneous visual change (eg, different color intensities or dye diffusion along a straight path), providing qualitative or semiquantitative information. Indicators are classified into 3 categories, namely time-temperature indicators, fresh indicators, and gas indicators.
Data carrier devices, also known as automatic identification devices, make information flow in the food supply chain more efficient, with the advantage of maintaining food quality and safety. Data carrier devices do not provide any information about the quality status of food but are intended for automation, traceability, theft prevention, or counterfeit protection. Data carrier devices in the food packaging industry are barcode labels and Radio Frequency Identification Data (RFID) tags, which fall into the main category of intelligent systems that increase convenience.
How does active packaging work?
The active packaging system is one of the packaging innovations that improve the functional properties of food packaging by releasing active substances in a specific and controlled method. Active packaging techniques for preservation, quality improvement, and food safety can be divided into two categories, namely scavenger systems and diffusion systems. The principle of the scavenger system is to remove unwanted components such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, ethylene, excess water, and other specific components. Oxygen scavengers, ethylene scavengers, and moisture absorbers are part of the scavenger system. The diffusion system or emitters principle is based on the release of the desired gas to the top of the packaging which has a positive impact on the packaged food, slowing down detrimental processes and extending shelf life. Carbon dioxide emitters, ethanol emitters, sulfur dioxide emitters, antioxidant release, and antimicrobial packaging are part of the diffusion or emitter system.
What are the strategies for managing smart packaging?
The sustainability of the supply chain, enhancement of the quality, safety, traceability, authentication, and integration will all benefit from the right strategy of smart packaging implementation. Strategy implementation must consider the concept of smart packaging that brings consumer perspective about the value-adding functional properties of smart packaging. Smart packaging has a functional value that can be categorized based on system, material, and techniques. The selection of packaging materials, technology, and techniques must be suitable to the characteristics and categories of food to provide a method that can manage and maintain smart packaging in food applications. Therefore, understanding the traditional and innovative packaging systems will be important for strategies toward smart packaging management. Traditional and innovative packaging systems can be seen in Figure 1.
How do you apply smart packaging in bread products?
Smart packaging application in bakery products, especially bread is one of the solutions to increase product shelf life. Shelf life extension can be done by adjustment formulation, processing and packaging to maintain and monitor critical quality parameters which affect staling. By combining interventions on bread formulation, processing, and packaging can be perceived daily and fresh bread quality for consumers. Combination formulation, processing, and smart packaging application to extend bread shelf life is determined in Figure 2.

Further reading
Smart Packaging Functionality and Benefits
How to Reduce Food Waste with Food Packaging?
Potential risks of food packaging plastic waste on human health and the environment
Reference
Yam, K. L., Takhistov, P. T., and Miltz, J. 2005. Intelligent packaging: concepts and applications. Journal of Food Science, 70-1: R1-R10.
Vanderroost, M., Ragaerta, P., Devliegherea, F., and De Meulenaer, B. 2014. Intelligent food packaging: The next generation. Trends in Food Science and Technology. 39: 47-62
Ahvenainen, R. 2003. Active and inteligent packaging: An introduction. Novel Food Packaging Techniques. CRC Press, Boca Raton, 5-21.
Robertson, 2012. Food Packaging: Principles and Practice, third ed. Florida Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton
Drago, E., Campardelli, R., Pettinato, M. and Perego, P. 2020. Innovations in Smart Packaging Concepts for Food: An Extensive Review. Foods, 9: 1628
Barska, A. and Joanna, W., 2016. Consumer perception of active and intelligent food packaging. Problems of Agricultural Economics, 4: 138–159.
Otles, S. and Yalcin, B. 2008. Intelligent food packaging. Log Forum 4, 4, 3
Amin, U., Khan, M.K.I., Maan, A.A., Nazir, A., Riaz, S., Khan, M.U., Sultan, M., Munekata, P.E.S., and Lorenzo, J.M. 2022. Biodegradable active, intelligent, and smart packaging materials for food applications. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 33: 100903
Chen, S., Brahma, S., Mackay, J., Cao, C., and Aliakbarian, B. 2020. The role of smart packaging system in food supply chain. Journal of Food Science, Vol. 0, Iss. 0, 2020
Lim, Loong-Tak. 2019. Active and Intelligent Packaging Materials. Comprehensive Biotechnology, 3rd edition, Volume 4
European Comission. 2004. REGULATION (EC) No 1935/2004 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 27 October 2004 on materials and articles intended to come into contact with food and repealing Directives 80/590/EEC and 89/109/EEC.
Ghaani, M., Cozzolino, C.A., Castelli, G. and Farris, S. 2016. An overview of the intelligent packaging technologies in the food sector. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 51: 1-11
Firouz, M.S., Mohi-Alden, K., and Omid, M. 2021. A critical review on intelligent and active packaging in the food industry: Research and development. Food Research International, 141: 110113
Galic, K., Gabric, D., and Curic, D. 2019. Packaging and the Shelf Life of Bread. Reference Module in Food Sciences. Page 1 – 8
Pasqualone, A. 2019. Bread Packaging: Features and Functions. Flour and Breads and their Fortification in Health and Disease Prevention. Page 211 – 222










































































