Banana Plant Care – Commercial Cultivation of Bananas

This post is also available in:
This post is also available in:
![]() Español (Spanish)
Español (Spanish) ![]() Français (French)
Français (French) ![]() Deutsch (German)
Deutsch (German) ![]() हिन्दी (Hindi)
हिन्दी (Hindi) ![]() العربية (Arabic)
العربية (Arabic) ![]() Türkçe (Turkish)
Türkçe (Turkish) ![]() Português (Portuguese (Brazil))
Português (Portuguese (Brazil))
How to Cultivate Bananas for Profit
Banana: Soil and Environmental requirements
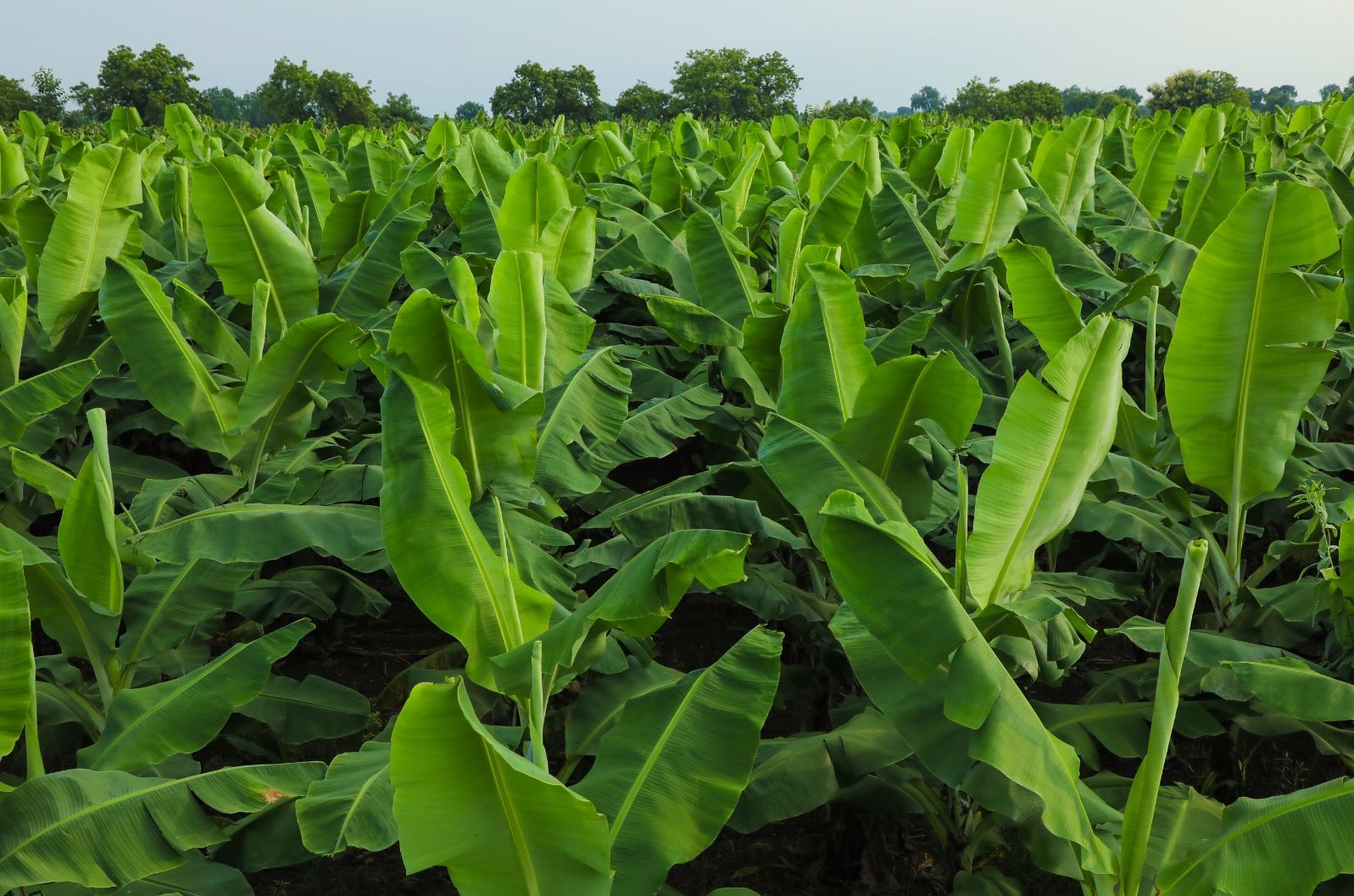
To simplify plant care, selecting the ideal planting location is necessary. Warm climates are excellent for growing the majority of banana plant species. This plant should be grown in a protected area away from strong winds because it is prone to leaf damage. You can prepare the planting area by incorporating some new compost into the soil and make sure you have enough space for your specific species-cultivars (height and spread) to grow.
Plant in a location that will receive full sun to achieve the best flowering and fruit growth. Bananas can grow in almost any soil except for sandy or swampy soils, which they cannot tolerate. The ideal soil is loose, free-draining, rich, and consistently moist.
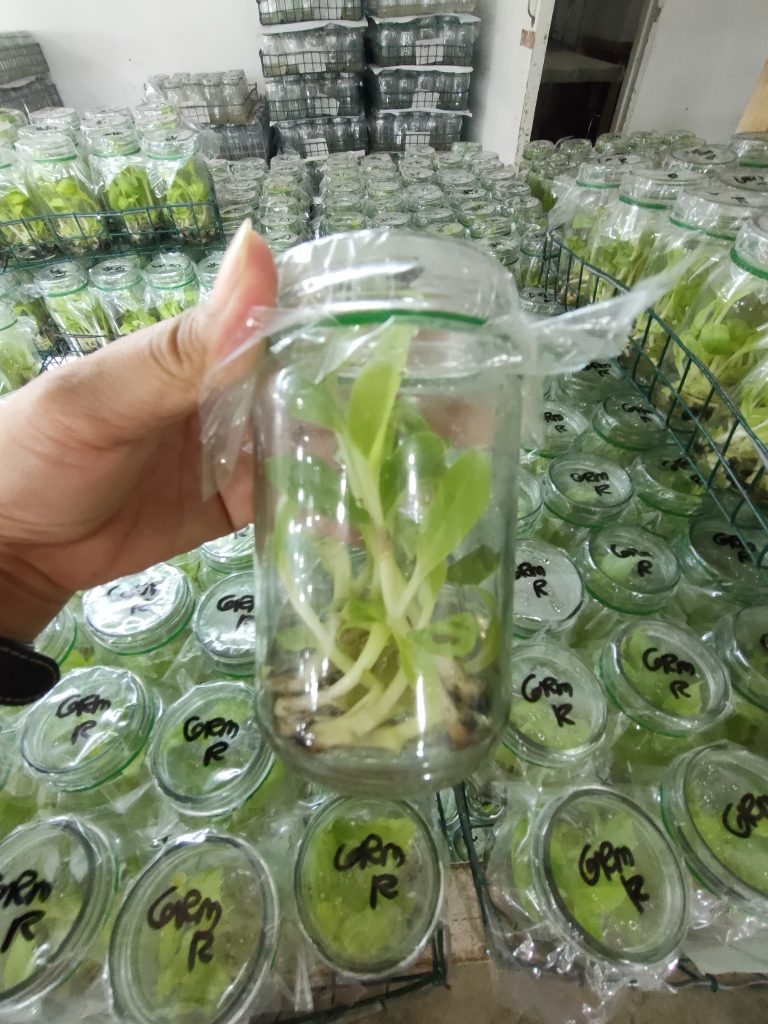
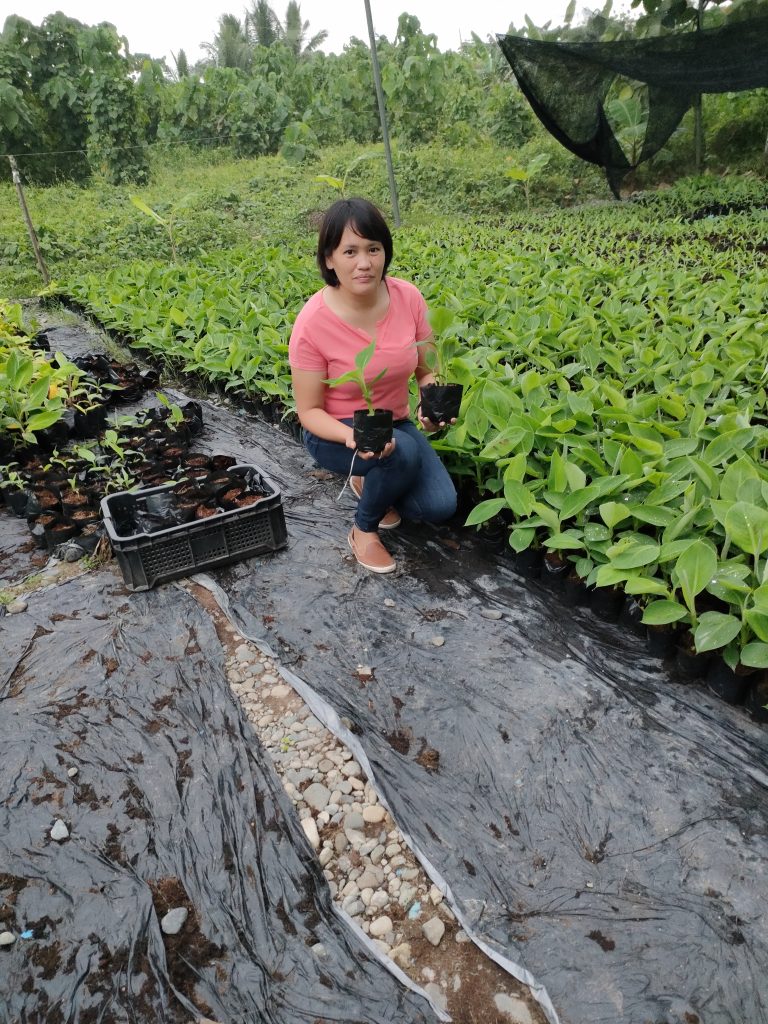


Banana Plant Propagation and Plant Nursery
Banana growers use various measures to control and prevent pests, weeds, and plant pathogens from spreading into new areas, especially through human interaction, such as international trade. It also follows standard operation to obtain good fruit quality.
In the field, there are two operations on how to care for banana plants: Plant care and Fruit care.
Plant Care
1 – Weed Management:It is the practice of removing weeds that compete with the banana plant for resources and serve as hosts for many crop parasites. In the early months after plantation, when the banana plants are young and there is minimal shade, weed control is crucial. Herbicide use can be decreased in commercial plantations when banana plants are grown on bare soil by spreading a ground cover (cover crop). There are different types of weeding:
- Chemical control
- Selective Chemical control
- Manual & Mechanical weeding
- Cover crop
2 – Fertilization: Requires regular feeding with both controlled-release fertilizer and organic matter, such as well-decomposed (well-rotted) manures. Both macro and micronutrients are essential for banana plant growth.
3 – Pest and Disease control:The primary tasks of this operation are the prevention, detection, diagnosis, and control-management of pests and diseases that can harm the crop.
Sigatoka control: Controlling the fungus (Mycosphaerella musicola) that causes Sigatoka leaf spot or Yellow Sigatoka, which spreads swiftly and can cause major damage, is a crucial task in the banana industry. Most farmers control the pathogen by spraying the banana canopy (young leaves) with a fungicide with an oil base.
4 – Population Management:Desuckering is crucial in commercial banana production. This process removes the undesirable suckers that grow close to the plant’s base. It is done by cutting the suckers at ground level and then using 2-3 drops of kerosene to kill the pseudostem’s growth point.
5 – Leaf Trimming: Another term for leaf trimming is deleafing; it is the practice of removing the unnecessary part of leaves, especially those infected by the Black Leaf streak caused by the fungus Mycosphaerella fijiensis.
Fruit Care
- Bud Injection/ Bud Tubing – One of the major operations in banana farming is to terminate or eliminate the infestation and the damage caused by Flower Thrips inside the buds of the banana.
- Bunch Spray – To eliminate the fungal and bacterial infections in the fruits.
- Early Bagging – To eliminate air-borne fungus and insects, bat and bird scratches damage at an early stage of fruit development.
- Deflowering/ Defingering – Removal of flowers from the tip of the finger of the hand. Defingering is the practice of removing deformed or excess fingers to obtain the good shape of the banana hand. Deflowering can be done in the field before bagging or during post-harvest operations.
- r recording harvestable bunches.
- Sok-sok Insertion – A hand bagging is a bunch protector and neck protectors to prevent point scars damage.
- Propping (Cable Guying/ Pole) – Giving plants the right support with bamboo is a fund
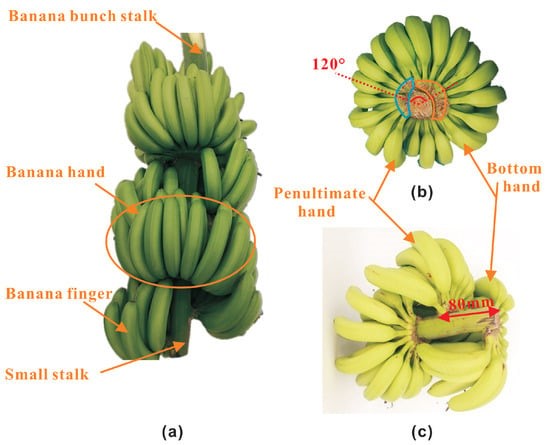
Xie et al., 2022
References
https://library.wur.nl/ojs/index.php/njas/article/view/17828/17242
https://bafs.da.gov.ph/bafs_admin/admin_page/pns_file/2021-02-24-PNS-BAFPS%20129-2013%20-%20GAP%20Banana(1).pdf
http://www.agritech.tnau.ac.in/expert_system/banana/Nutrientmgmt.html
Xie B, Jin M, Duan J, Yang Z, Xu S, Luo Y, Wang H. Design and Analysis of a Flexible Adaptive Supporting Device for Banana Harvest. Agronomy. 2022; 12(3):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030593
Further reading
Banana: Crop History, Nutritional Value and Health Benefits
Banana Plant Information & Environmental Requirements
Banana Plant Care – Commercial Cultivation of Bananas
Soil Requirements and Land Preparation for Bananas
Banana Planting Distances and Support Systems
Banana Water Requirements & Irrigation Systems
Banana Nutrient Requirements and Fertilization Program
Banana Plant Protection – Major Banana Diseases
Banana Plant Protection – Common Pests of Banana Plants








































































